Introduction
Data backup is an important process that helps businesses keep their data safe and reduce the chance of losing data. When you back up data, you make a copy of it and store it in a different place to protect it from things like hardware failures, natural disasters, cyber attacks, and other things you can’t plan for. The data backup storage can be off-site or on-site like tape library, virtual disk library, SAN/NAS storage or public cloud storage etc. In this blog, we’ll talk about backing up data and the data backup types.
Types of Backups
Businesses can protect their data with different types of data backup method. These are as below:
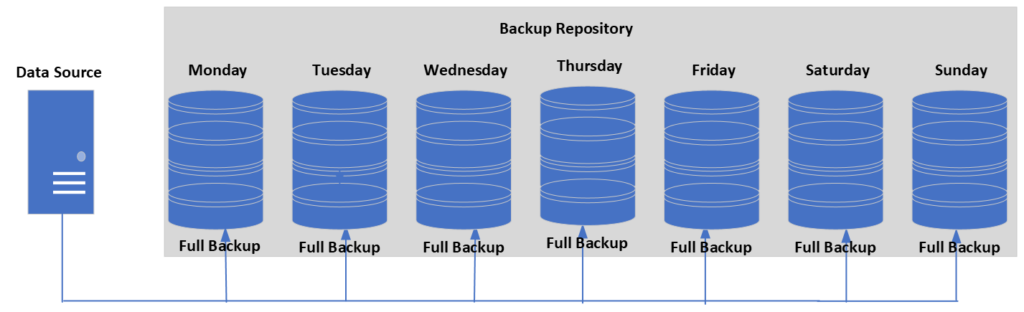
Full Backup
A full backup is a copy of all of the information on a system. This kind of backup is usually done on a regular schedule, like once a day, once a week, or once a month, depending on how much data there is and the business’s backup policy.
For example, a business might do a full backup of its accounting system every day to make sure that all of its financial data is backed up and safe in case the system fails or something else happens.
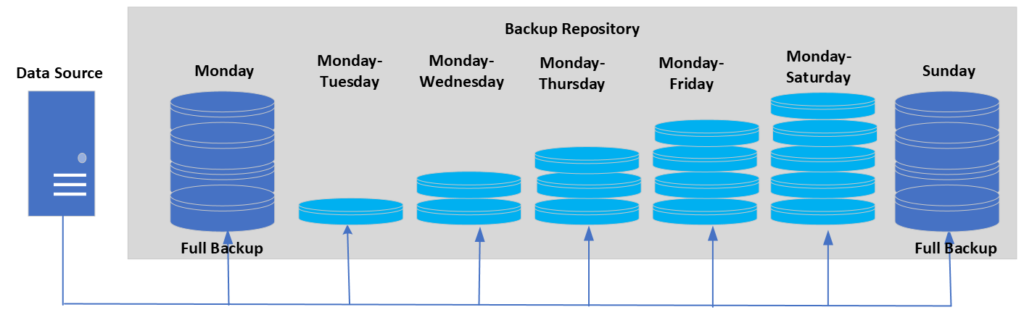
Differential Backup
A differential backup only backs up the data that has changed since the last full backup. This type of backup is faster than a full backup, and takes up less space than an incremental backup every day. After full backup all increments and changes are added to create a backup. Simply put differential backup add up to latest changes backed up. It let us restore data quickly.
For example, a business might do a differential backup of its customer database every day to make sure that data of all new customers are safe and recoverable in case of a system failure or other problem.
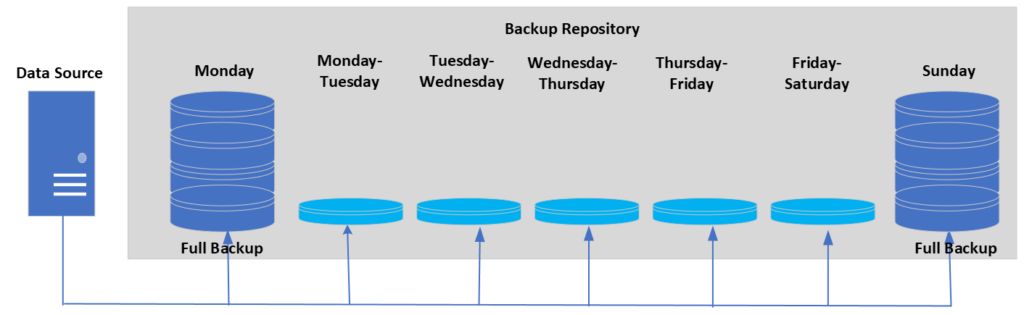
Incremental Backup
A backup of only the data that has changed since the last full or only changes of data backed up is called an incremental backup. This type of backup only saves the changes that have been made since the most recent backup. This makes backups taking less time and take up less space.
For example, a business might do an incremental backup of their email server every hour to make sure that data of all new emails are safe and recoverable in case of a hardware failure or other problem.
Mirror Backup
A mirror backup is a copy of the data on a system that is exactly the same as the original data. Mission-critical systems or data requires that kind of mirrored copy to restore quickly in case of any data loss occurrence.
For example, a business might do a mirror backup of their web server every day to make sure that backup of all website data is available and safe in case of a cyber attack or other incident.
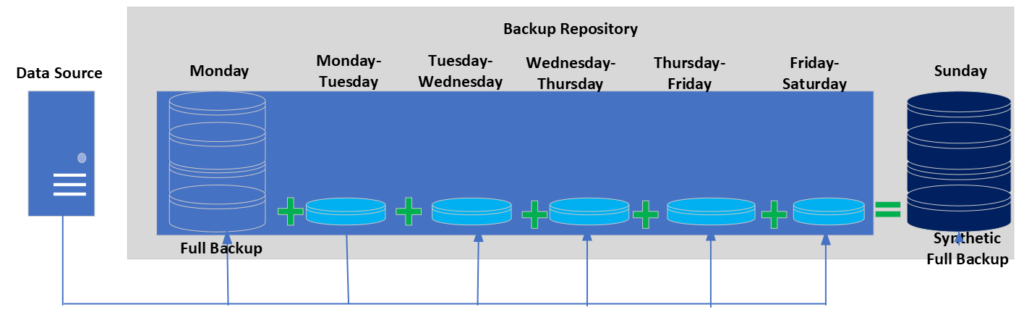
Synthetic Full Backup
This method creates a new full backup by combining data from an existing full backup and incremental backups. A conventional full backup copies all of the source system’s data to the backup storage. This can require a considerable amount of time and resources. Synthetic full backup does not always perform a full backup from the client. In contrast, synthetic full backup combines a full backup with one or more incremental backups.
The data from the full backup stored added to followed by the application of the changes from the incremental backups . So, the result is a new backup that contains all of the source system’s data, similar to a traditional full backup. Traditional full backups are slower and require more storage space than synthetic full backups.
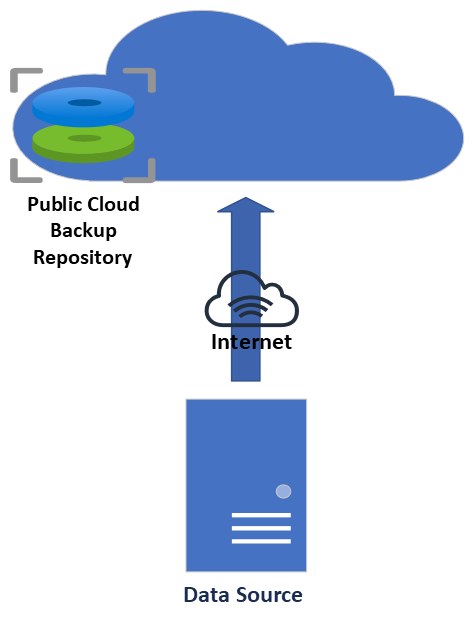
Cloud Backup
Cloud backup is a way to back up your data that stores it in the cloud based backup repository. Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform are options available. This enables businesses to back up their data that aren’t on-site and able to bring back online.
For example, a business might use a cloud backup solution to store all of its business data, like financial records, customer records, and employee records, in a secure cloud-based service.
Comparison
| Full | Differential | Incremental | Synthetic Full | Mirror | Cloud | |
| Storage Space | High | Medium ~ High | Low | Medium ~ High | Same as Source | Depending on source data and backup policy |
| Backup Speed | Slower | Fast | Faster | Fast | Faster | Depending on Internet Speed and medium-Generally Slower |
| Restore Speed | Faster | Fast | Slower | Faster | Faster | Depending on Internet Speed and medium -Generally Slower |
| Recovery Media | Recent only | Recent full + only recent incremental to full | Full + all incremental backups to full | Recent only | Recent only | Depending upon backup policy |
Conclusion
Data backup is an important process that helps businesses keep their data safe and reduce the chance of losing data. Businesses can create a full backup strategy using different types of data backup solutions. Backup strategy enables business in protecting their data and ensures business continuity in case of a disaster. Data backup gives assurance to businesses that data is safe and recoverable in case of any data loss event. There are different methods available like full backups, incremental backups, differential backups, mirror backups, or cloud backup solutions. Moreover,Every type of data backup method has its pros and cons and opted to depend upon the business data’s nature, criticality, privacy and availability requirements.
Good article. I will be experiencing a few of these issues
as well..